What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common condition that causes pain, numbness, and tingling in the hand and arm. The condition occurs when the median nerve – one of the major nerves to the hand – is squeezed or compressed as it travels through the wrist. In addition to the numbness and tingling, carpal tunnel syndrome can cause swelling, weakness, and nighttime pain. Patients sometimes describe dropping things unexpectedly and may have difficulty with buttoning shirts, tying shoelaces, or handling loose change.
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is frequently seen in individuals who develop swelling or inflammation in their hands. People who smoke, as well as those with connective tissue diseases, diabetes mellitus, and hypothyroidism, may be at greater risk. The median nerve acts as an electrical wire between the spinal cord and the hand. The nerve passes through the carpal tunnel in the wrist, along with nine tendons that bend the fingers.
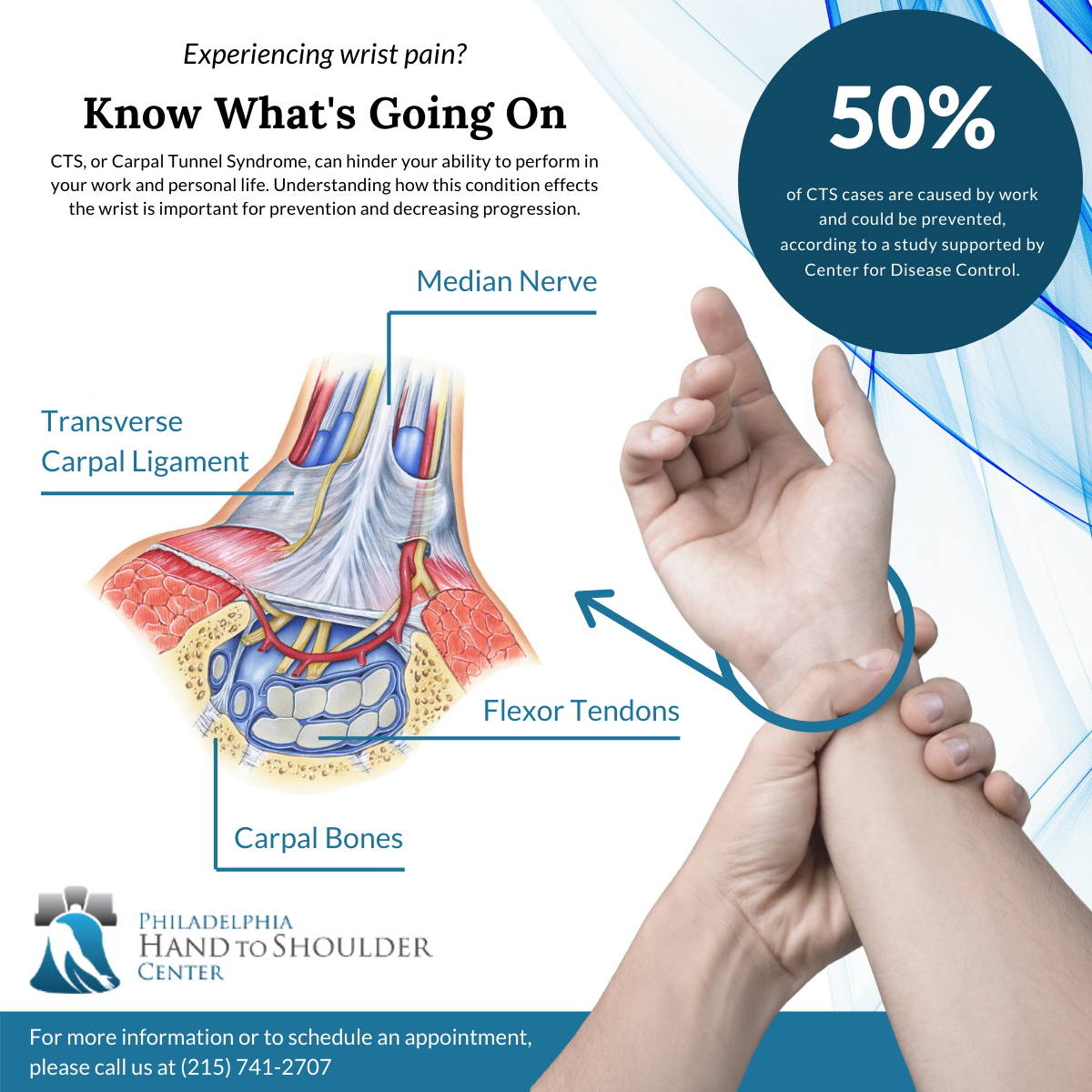
When the tendons in the wrist become swollen and inflamed, the median nerve can become compressed by the transverse carpal ligament (see figure), leading to carpal tunnel symptoms. Early on, symptoms commonly occur during sleeping hours. In more advanced cases, the symptoms can become problematic during waking hours. Many sufferers describe symptoms with common activities, like reading the newspaper or driving a car.
What Can a Hand Surgeon do to Help?
A hand surgeon can order special nerve tests to verify the extent of the problem. Custom wrist splints are helpful for the early stages of carpal tunnel syndrome. These splints are worn at nighttime to relieve pressure on the median nerve and to prevent the wrists from bending during sleep. Cortisone injections often provide excellent relief from symptoms. Unfortunately, symptomatic relief is only temporary, and most people experience a recurrence of symptoms after 3-4 months. For chronic or more advanced cases, carpal tunnel surgery is often recommended as the best course of treatment.
What Can I Expect From Surgery?
Surgery provides more space for the median nerve and relieves pressure on the median nerve and tendons. This procedure is typically done under light sedation and local anesthesia, and usually takes only minutes to complete. The minimally invasive approach minimizes discomfort following surgery and allows patients to return to activities more quickly. Over 95% of patients improve dramatically following surgical intervention, with most returning to daily activities within days. Many patients can resume heavier job-related activities after 2-4 weeks.

Recent Comments